
The disaster in Yemen has steadily escalated in recent weeks with the Houthi missile and drone attacks on Saudi Arabia and the UAE and the retaliatory airstrikes by the Saudi-led coalition on the Houthi-held territories in Yemen. The worsening crisis with larger geopolitical importance for the Gulf region has brought up issues on what the international community, especially the UN, has committed to resolving the issue. While the UN has failed to find a lasting ceasefire, let alone a settlement to the conflict, its different agencies have been working in Yemen since the crisis broke out in early 2011.
Background of this war
One of the Arab world’s poorest countries, Yemen has been destroyed by a near seven-year civil war, which started after Houthis captured the capital Sana’a, following which Saudi-led forces intervened and fought the rebels to end Iranian influence in the region and restore the former government.
- The UAE joined the Saudi campaign in 2015 and has been deeply involved in the conflict ever since, despite announcing the formal withdrawal of its forces in 2019 and 2020.
Who are the Houthis?
Founded in the 1990s by Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, a member of Yemen’s Shia majority.
It is a group of Zaidi Shia Muslims who ruled a kingdom in the province for nearly 1,000 years.
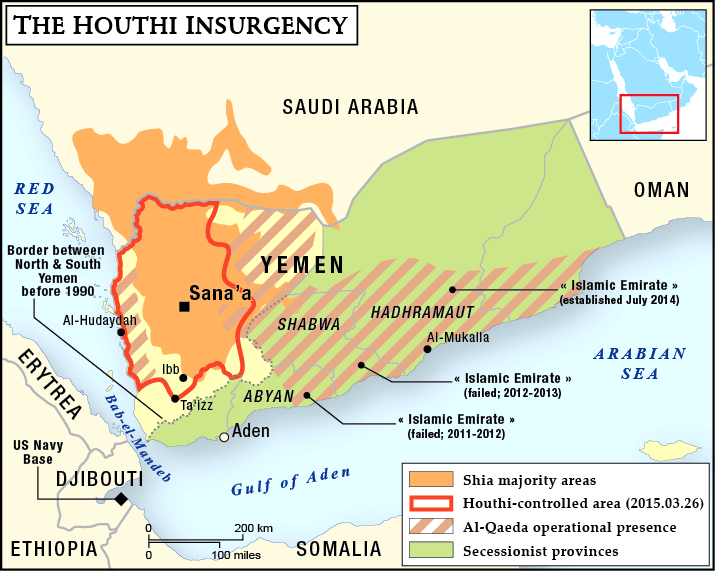
- The confrontation has its origins in the Arab Spring of 2011, when an uprising forced the country’s long-time authoritarian president, Ali Abdullah Saleh, to hand over power to his deputy, Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi.
- The political transition was supposed to bring stability to Yemen, one of the Middle East’s poorest nations, but President Hadi struggled to deal with various problems including militant attacks, corruption, food insecurity, and continuing loyalty of many military officers to Saleh.
- Fighting began in 2014 when the Houthi Shia Muslim rebel movement took advantage of the new president’s weakness and seized control of northern Saada province and neighbouring areas.
Saudi Arabia intervened in Yemen after the Shia Houthi rebels captured Sana’a, the capital city, and the internationally accepted government of President Hadi moved to the country’s south.
- The rapid rise of the Houthis in Yemen set off alarm bells in Saudi Arabia which saw them as Iranian proxies.
- Saudi Arabia started a military campaign in March 2015, hoping for a quick victory against the Houthis. But the Houthis had dug in, refusing to leave despite Saudi Arabia’s aerial blitzkrieg.
- With no effective allies on the ground and a no-way-out plan, the Saudi-led campaign went on with no tangible result. In the past six years, the Houthis have launched multiple attacks on Saudi cities from northern Yemen in retaliation for Saudi airstrikes.
- Since the Saudi intervention in 2015, at least 10,000 people have been killed in Yemen, according to the WHO. The widespread damage caused to infrastructure by the coalition airstrikes and lack of supplies of food and medicines due to the blockade has pushed Yemen into a humanitarian catastrophe. About 12 million people are at risk of starvation if aid doesn’t reach them fast. The country has also seen a massive cholera outbreak. A child dies every 10 minutes in Yemen from preventable causes, says UNICEF.
What is the role of the UN?
In April 2011, the UN-appointed a Special Advisor to the Secretary-General on Yemen. The Special Advisor played a significant role in mediating the early negotiations between warring parties in the southern Arabian country. He met with Yemeni leaders, foreign diplomats, and the Yemenis demonstrating in squares around Sana’a. These negotiations later promoted the signing of the first political transition agreement, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Initiative, and its Implementation Mechanism, in November 2011.
In 2012, the UN formed a special political mission for Yemen by establishing the Office of the Special Envoy to the Secretary-General on Yemen. The Special Envoy is responsible for engaging with all sides in Yemen, including the Government, political parties, civil societies and working closely with other regional and international actors to facilitate the political transition on behalf of the UN Secretary-General. The Special Envoy briefs the Security Council regularly on the peace process and the situation in Yemen.
Negotiations led by the Office of the Special Envoy enabled the Yemenis to conclude a National Dialogue Conference in 2014, seeking a new federal and democratic Yemen. The Office of the Special Envoy provided diplomatic, political, technical, logistical, and financial support for the national dialogue process. It also facilitated dozens of Dialogue sessions at the interlocutors’ request. Since 2015, the Office has mediated four rounds of talks between the Yemeni warring factions in Geneva (June 2015), Bienne (December 2015), Kuwait (April to August 2016), and Stockholm (December 2018). The Special Envoy played a crucial role in facilitating the Stockholm Agreement that agreed to a ceasefire (Hodeidah Agreement), opening humanitarian corridors (Taiz understanding), and a prisoner swap.
The Houthi’s reply has been to fire ballistic missiles and explosive-laden drones, first on Saudi Arabia and now on the UAE.
UAE and US militaries said they intercepted two ballistic missiles over Abu Dhabi. The rebels said they targeted the Al-Dhafra Air Base, which hosts both American and British forces.
we write articles from top news sources of India and international news web portals. Because to understand the topics in a depth we need to read more than one source for the UPSC IAS exam. So every article got credit to PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Business Standard,NDTV, CNN, etc. And the conclusion of this article is also available on our youtube channel. Thanks for your love and support and queries and suggestions just mail us at [email protected].
